Android Fragment里嵌入高德地图定位
在上一篇已经写了嵌入高德地图,这里来说一下怎么实现定位,并显示定位的图标。
public class FragmentMap extends Fragment implements LocationSource, AMapLocationListener{
private static FragmentMap fragment = null;
@ViewInject(R.id.map)
private MapView mapView;
private AMap aMap;
private View mapLayout;
private OnLocationChangedListener mListener;
private LocationManagerProxy mAMapLocationManager;
public static Fragment newInstance() {
if (fragment == null) {
synchronized (FragmentMap.class) {
if (fragment == null) {
fragment = new FragmentMap();
}
}
}
return fragment;
}
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
if (mapLayout == null) {
mapLayout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_map, null);
ViewUtils.inject(this, mapLayout);
mapView.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
if (aMap == null) {
aMap = mapView.getMap();
aMap.setLocationSource(this);// 设置定位监听
aMap.getUiSettings().setMyLocationButtonEnabled(true);// 设置默认定位按钮是否显示
aMap.setMyLocationEnabled(true);// 设置为true表示显示定位层并可触发定位,false表示隐藏定位层并不可触发定位,默认是false
// 自定义系统定位蓝点
MyLocationStyle myLocationStyle = new MyLocationStyle();
// 自定义定位蓝点图标
myLocationStyle.myLocationIcon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromResource(R.mipmap.content_btn_location));
// 将自定义的 myLocationStyle 对象添加到地图上
aMap.setMyLocationStyle(myLocationStyle);
// 构造 LocationManagerProxy 对象
mAMapLocationManager = LocationManagerProxy.getInstance(getActivity());
}
} else {
if (mapLayout.getParent() != null) {
((ViewGroup) mapLayout.getParent()).removeView(mapLayout);
}
}
return mapLayout;
}
@Override
public void onAttach(Activity activity) {
super.onAttach(activity);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}
@Override
public void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mapView.onResume();
}
/**
* 方法必须重写
* map的生命周期方法
*/
@Override
public void onPause() {
super.onPause();
mapView.onPause();
deactivate();
}
/**
* 方法必须重写
* map的生命周期方法
*/
@Override
public void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState) {
super.onSaveInstanceState(outState);
mapView.onSaveInstanceState(outState);
}
/**
* 方法必须重写
* map的生命周期方法
*/
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
mapView.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public void onLocationChanged(AMapLocation aMapLocation) {
if (mListener != null && aMapLocation != null) {
if (aMapLocation.getAMapException().getErrorCode() == 0) {
mListener.onLocationChanged(aMapLocation);// 显示系统小蓝点
//获取位置信息
geoLat = aMapLocation.getLatitude();
geoLng = aMapLocation.getLongitude();
aMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.zoomTo(14));
}
}
}
@Override
public void onLocationChanged(Location location) {
}
@Override
public void onStatusChanged(String provider, int status, Bundle extras) {
}
@Override
public void onProviderEnabled(String provider) {
}
@Override
public void onProviderDisabled(String provider) {
}
//激活定位
@Override
public void activate(OnLocationChangedListener listener) {
mListener = listener;
if (mAMapLocationManager == null) {
mAMapLocationManager = LocationManagerProxy.getInstance(getActivity());
//此方法为每隔固定时间会发起一次定位请求,为了减少电量消耗或网络流量消耗,
//注意设置合适的定位时间的间隔,并且在合适时间调用removeUpdates()方法来取消定位请求
//在定位结束后,在合适的生命周期调用destroy()方法
//其中如果间隔时间为-1,则定位只定一次
mAMapLocationManager.requestLocationData(LocationProviderProxy.AMapNetwork, 60 * 1000, 10, this);
}
}
//停止定位
@Override
public void deactivate() {
mListener = null;
if (mAMapLocationManager != null) {
mAMapLocationManager.removeUpdates(this);
mAMapLocationManager.destroy();
}
mAMapLocationManager = null;
}
} Android开发之 Fragment里嵌入高德地图非常的简单了我们一起来看一个实现的例子,具体如下所示。 最近在做的项目里要用到地图,看了一下高德地图的API,最后决定就用高德地图,和平时不同,这次地图是要嵌在Fragment了,研究了一下网上的代码,最后实现了。下面说一下实现2D地图的方法。
1.先去高德地图官网注册Key,地址是http://lbs.amap.com/api/android-sdk/summary/;
2.根据说明下载所需的sdk.
![]()
3.配置工程
(1)添加key
在工程的“ AndroidManifest.xml ”文件如下代码中添加Key.
(1)添加权限
<pre><code><uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CHANGE_WIFI_STATE" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CHANGE_CONFIGURATION" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS" /></code></pre>
4.布局文件
<com.amap.api.maps2d.MapView android:id="@+id/map" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" />
5.实现
public class FragmentMap extends Fragment{
private static FragmentMap fragment = null;
@ViewInject(R.id.map)
private MapView mapView;
private AMap aMap;
private View mapLayout;
public static Fragment newInstance() {
if (fragment == null) {
synchronized (FragmentMap.class) {
if (fragment == null) {
fragment = new FragmentMap();
}
}
}
return fragment;
}
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
if (mapLayout == null) {
mapLayout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_map, null);
ViewUtils.inject(this, mapLayout);
mapView.onCreate(savedInstanceState);//必须写
if (aMap == null) {
aMap = mapView.getMap();
} else {
if (mapLayout.getParent() != null) {
((ViewGroup) mapLayout.getParent()).removeView(mapLayout);
}
}
return mapLayout;
}
@Override
public void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mapView.onResume();
}
/**
* 方法必须重写
* map的生命周期方法
*/
@Override
public void onPause() {
super.onPause();
mapView.onPause();
}
/**
* 方法必须重写
* map的生命周期方法
*/
@Override
public void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState) {
super.onSaveInstanceState(outState);
mapView.onSaveInstanceState(outState);
}
/**
* 方法必须重写
* map的生命周期方法
*/
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
mapView.onDestroy();
}
}
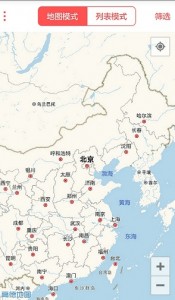
效果图如下:
下文为各位重点介绍关于Android高德地图自定义Markers的例子,希望这篇文章能够让各位理解到Android高德地图自定义Markers的方法。
之前的博客里说了地图的嵌入和定位,今天就说说在地图上显示一些我们想要的。在地图中有自带的Markers(标记),但是它只显示一个椭圆的图标,一般是不符合我们的需求的,这样就要我们自己来自定义。首先标记有下面一些属性;
1.position(Required) 在地图上标记位置的经纬度值。参数不能为空。
2.title 当用户点击标记,在信息窗口上显示的字符串。
3.snippet 附加文本,显示在标题下方。
4.draggable 如果您允许用户可以自由移动标记,设置为“ true ”。默认情况下为“ false ”。
5.visible 设置“ false ”,标记不可见。默认情况下为“ true ”。
6.anchor图标摆放在地图上的基准点。默认情况下,锚点是从图片下沿的中间处。
7.perspective设置 true,标记有近大远小效果。默认情况下为 false。
8.可以通过Marker.setRotateAngle() 方法设置标记的旋转角度,从正北开始,逆时针计算。如设置旋转90度,Marker.setRotateAngle(90)
9.通过setFlat() 方法设置标志是否贴地显示
自定义图标通常由 BitmapDescriptor 设置。我们可以在类 BitmapDescriptorFactory 使用以下其中一种方法定义。
1.fromAsset(String assetName) 在 assets 目录中使用图像创建自定义标记。
2.fromBitmap (Bitmap image) 使用位图图像创建自定义标记。
3.fromFile (String path) 指定路径的文件创建自定义图标。
4.fromResource (int resourceId) 使用已经存在的资源创建自定义图标。
先看一下要实现的效果:
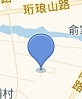 地图自带标记
地图自带标记  实现效果
实现效果
实现思路是:自定义布局,获取数据填入相应位置,然后将view转成Bitmap,调用AMap.addMarker(markerOptions) 方法添加到地图上。
自定义布局并填充数据:
for (int i = 0; i < positionEneityList.size(); i++) {
if (positionEneityList.get(i).getType().equals("1")) {
View view = View.inflate(getActivity(),R.layout.view_day, null);
TextView tv_price = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tv_price);
TextView tv_price_status = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tv_price_status);
tv_price.setText(positionEneityList.get(i).getPrice());
tv_price_status.setText("元/时");
Bitmap bitmap = CommentActivity.convertViewToBitmap(view);
drawMarkerOnMap(new LatLng(Double.parseDouble(positionEneityList.get(i).getLatitude())
, Double.parseDouble(positionEneityList.get(i).getLongitude())), bitmap, positionEneityList.get(i).getId());
}
}
2.转成Bitmap:
//view 转bitmap
public static Bitmap convertViewToBitmap(View view) {
view.measure(View.MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(0, View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED), View.MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(0, View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED));
view.layout(0, 0, view.getMeasuredWidth(), view.getMeasuredHeight());
view.buildDrawingCache();
Bitmap bitmap = view.getDrawingCache();
return bitmap;
}3.添加到地图上:
/**
* 在地图上画marker
*
* @param point marker坐标点位置(example:LatLng point = new LatLng(39.963175,
* 116.400244); )
* @param markerIcon 图标
* @return Marker对象
*/
private Marker drawMarkerOnMap(LatLng point, Bitmap markerIcon, String id) {
if (aMap != null && point != null) {
Marker marker = aMap.addMarker(new MarkerOptions().anchor(0.5f, 1)
.position(point)
.title(id)
.icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromBitmap(markerIcon)));
return marker;
}
return null;
}
这样就实现了上述效果。
上一篇说了在地图上实现了自定义Markers,但是markers太多在地图上显示的就会密密麻麻,重叠覆盖,这里就介绍一下markers的聚合。先看一下封装好的聚合类。
public class MarkerClusterYellow {
private Activity activity;
private MarkerOptions options;
private ArrayList<MarkerOptions>includeMarkers;
private LatLngBounds bounds;// 创建区域
/**
*
* @param activity
* @param firstMarkers
* @param projection
* @param gridSize
* 区域大小参数
*/
public MarkerClusterYellow(Activity activity, MarkerOptions firstMarkers,
Projection projection, int gridSize) {
options = new MarkerOptions();
this.activity = activity;
Point point = projection.toScreenLocation(firstMarkers.getPosition());
Point southwestPoint = new Point(point.x - gridSize, point.y + gridSize);
Point northeastPoint = new Point(point.x + gridSize, point.y - gridSize);
bounds = new LatLngBounds(
projection.fromScreenLocation(southwestPoint),
projection.fromScreenLocation(northeastPoint));
options.anchor(0.5f, 0.5f).title(firstMarkers.getTitle())
.position(firstMarkers.getPosition())
.icon(firstMarkers.getIcon())
.snippet(firstMarkers.getSnippet());
includeMarkers = new ArrayList<MarkerOptions>();
includeMarkers.add(firstMarkers);
}
/**
* 添加marker
*/
public void addMarker(MarkerOptions markerOptions) {
includeMarkers.add(markerOptions);// 添加到列表中
}
/**
* 设置聚合点的中心位置以及图标
*/
public void setpositionAndIcon(String text) {
String id="";
int size = includeMarkers.size();
if (size == 1) {
return;
}
double lat = 0.0;
double lng = 0.0;
String snippet = "";
for (MarkerOptions op : includeMarkers) {
lat += op.getPosition().latitude;
lng += op.getPosition().longitude;
snippet += op.getTitle() + "\n";
id=id+op.getTitle()+",";
}
options.position(new LatLng(lat / size, lng / size));// 设置中心位置为聚集点的平均距离
options.title(id);
options.snippet(snippet);
int iconType = size / 2;
switch (iconType) {
default:
options.icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory
.fromBitmap(getViewBitmap(getView(size,text,
R.mipmap.content_icon_positions_yellow))));
break;
}
}
public LatLngBounds getBounds() {
return bounds;
}
public MarkerOptions getOptions() {
return options;
}
public void setOptions(MarkerOptions options) {
this.options = options;
}
public View getView(int carNum,String text,int resourceId) {
View view = activity.getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.my_car_cluster_view, null);
TextView carNumTextView = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.my_car_num);
TextView tv_price = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tv_price);
TextView tv_price_status = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tv_price_status);
tv_price.setText(text);
tv_price_status.setText("元/天");
tv_price.setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#FFBB18"));
tv_price_status.setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#FFBB18"));
LinearLayout myCarLayout = (LinearLayout) view.findViewById(R.id.my_car_bg);
myCarLayout.setBackgroundResource(resourceId);
carNumTextView.setText(String.valueOf(carNum));
return view;
}
/**
* 把一个view转化成bitmap对象
*/
public static Bitmap getViewBitmap(View view) {view.measure(MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(0, MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED),
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(0, MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED));
view.layout(0, 0, view.getMeasuredWidth(), view.getMeasuredHeight());
view.buildDrawingCache();
Bitmap bitmap = view.getDrawingCache();
return bitmap;
}
}在前一篇博客的基础上我们进行聚合,只需要做以下操作:
public class FragmentMap extends Fragment implements LocationSource, AMapLocationListener,OnCameraChangeListener {
private static FragmentMap fragment = null;
@ViewInject(R.id.map)
private MapView mapView;
private AMap aMap;
private View mapLayout;
private OnLocationChangedListener mListener;
private LocationManagerProxy mAMapLocationManager;
private List<PositionEneity> positionEneityList = new ArrayList<PositionEneity>();
private ArrayList<MarkerOptions> markerOptionsListYellow = new ArrayList<MarkerOptions>();// 所有的marker
private ArrayList<MarkerOptions> markerOptionsListInViewYellow= new ArrayList<MarkerOptions>();// 视野内的marker
String yellow="";
private int height;// 屏幕高度(px)
private int width;// 屏幕宽度(px)
private int gridSize = 50;// marker点区域大小
Handler handler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(android.os.Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
if (msg.what == 0) {
resetMarks();// 更新markers
}
}
};
public static Fragment newInstance() {
if (fragment == null) {
synchronized (FragmentMap.class) {
if (fragment == null) {
fragment = new FragmentMap();
}
}
}
return fragment;
}
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,Bundle savedInstanceState) {
if (mapLayout == null) {
mapLayout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_map, null);
ViewUtils.inject(this, mapLayout);
mapView.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
DisplayMetrics dm = new DisplayMetrics();
getActivity().getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(dm);
width = dm.widthPixels;
height = dm.heightPixels;
if (aMap == null) {
aMap = mapView.getMap();
aMap.setLocationSource(this);// 设置定位监听
aMap.getUiSettings().setMyLocationButtonEnabled(true);// 设置默认定位按钮是否显示
aMap.setMyLocationEnabled(true);// 设置为true表示显示定位层并可触发定位,false表示隐藏定位层并不可触发定位,默认是false
}
} else {
if (mapLayout.getParent() != null) {
((ViewGroup) mapLayout.getParent()).removeView(mapLayout);
}
}
aMap.setOnCameraChangeListener(this);
return mapLayout;
}
/**
* 获取视野内的marker 根据聚合算法合成自定义的marker 显示视野内的marker
*/
<strong> private void resetMarks() {
// 开始刷新界面
Projection projection = aMap.getProjection();
Point p = null;
markerOptionsListInViewYellow.clear();
// 获取在当前视野内的marker;提高效率
for (MarkerOptions mp : markerOptionsListYellow) {
p = projection.toScreenLocation(mp.getPosition());
if (p.x < 0 || p.y < 0 || p.x > width || p.y > height) {
// 不添加到计算的列表中
} else {
markerOptionsListInViewYellow.add(mp);
}
}
// 自定义的聚合类MarkerCluster
ArrayList<MarkerClusterYellow> clustersMarkeryellow = new ArrayList<MarkerClusterYellow>();
for (MarkerOptions mp : markerOptionsListInViewYellow) {
if (clustersMarkeryellow.size() == 0) {
clustersMarkeryellow.add(new MarkerClusterYellow(getActivity(), mp,
projection, gridSize));//gridSize 根据自己需求调整
} else {
boolean isIn = false;
for (MarkerClusterYellow cluster : clustersMarkeryellow) {
if (cluster.getBounds().contains(mp.getPosition())) {
cluster.addMarker(mp);
isIn = true;
break;
}
}
if (!isIn) {
clustersMarkeryellow.add(new MarkerClusterYellow(getActivity(), mp, projection, gridSize));
}
}
}
// 先清除地图上所有覆盖物
aMap.clear();
for (MarkerClusterYellow markerClusterYellow : clustersMarkeryellow) {
markerClusterYellow.setpositionAndIcon(yellow);// 设置聚合点的位置和icon
aMap.addMarker(markerClusterYellow.getOptions());// 重新添加
}
}
private void initview() {
for (int i = 0; i < positionEneityList.size(); i++) {
if (positionEneityList.get(i).getType().equals("2")) {
yellow=positionEneityList.get(i).getPrice();
View view01 = View.inflate(getActivity(),R.layout.view_everyday, null);
TextView tv_price = (TextView) view01.findViewById(R.id.tv_price);
TextView tv_price_status = (TextView) view01.findViewById(R.id.tv_price_status);
tv_price.setText(positionEneityList.get(i).getPrice());
tv_price_status.setText("元/天");
Bitmap bitmap = CommentActivity.convertViewToBitmap(view01);
<strong> markerOptionsListYellow.add(new MarkerOptions() .position(new LatLng(Double.parseDouble(positionEneityList.get(i).getLatitude())
, Double.parseDouble(positionEneityList.get(i).getLongitude()))).icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.fromBitmap(bitmap))
.title(positionEneityList.get(i).getId()));
}
}
}
@Override
public void onCameraChange(CameraPosition cameraPosition) {
}
@Override
public void onCameraChangeFinish(CameraPosition cameraPosition) {
handler.sendEmptyMessage(0);// 更新界面marker
}
}
定位和地图显示部分请参考之前的博客:
为了解决android手机适配问题,我们经常想如果可以按照百分比的方式进行界面布局,这样适配各种屏幕就简单多了吧!现在谷歌正式提供百分比布局支持库(android-support-percent-lib)。
这个库提供了:
两种布局供大家使用: PercentRelativeLayout、PercentFrameLayout,通过名字就可以看出,这是继承自FrameLayout和RelativeLayout两个容器类;
支持的属性有:
layout_widthPercent、layout_heightPercent、
layout_marginPercent、layout_marginLeftPercent、
layout_marginTopPercent、layout_marginRightPercent、
layout_marginBottomPercent、layout_marginStartPercent、layout_marginEndPercent。
可以看到支持宽高,以及margin。
也就是说,大家只要在开发过程中使用PercentRelativeLayout、PercentFrameLayout替换FrameLayout、RelativeLayout即可。
使用:
关于使用,其实及其简单,并且github上也有例子,android-percent-support-lib-sample。
使用Android studio在build.gradle添加以下信息就可以获取支持库,当然了,如果你没有下载到该支持库会提示你下载。
{5330C3E9-D43A-40E0-A247-83C217BE9A84}
PercentRelativeLayout使用小例子:
布局文件如下:
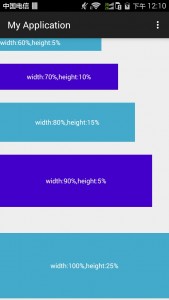
<android.support.percent.PercentRelativeLayout xmlns:android=" http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android " xmlns:app=" http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto " android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TextView android:id="@+id/row_one_item_one" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:background="#7700ff00" android:text="w:70%,h:20%" android:gravity="center" app:layout_heightPercent="20%" app:layout_widthPercent="70%"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/row_one_item_two" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/row_one_item_one" android:background="#396190" android:text="w:30%,h:20%" app:layout_heightPercent="20%" android:gravity="center" app:layout_widthPercent="30%"/> <ImageView android:id="@+id/row_two_item_one" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0dp" android:scaleType="centerCrop" android:layout_below="@+id/row_one_item_one" android:background="#d89695" app:layout_heightPercent="70%"/> <TextView android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_below="@id/row_two_item_one" android:background="#770000ff" android:gravity="center" android:text="width:100%,height:10%" app:layout_heightPercent="10%" app:layout_widthPercent="100%"/> </android.support.percent.PercentRelativeLayout
效果图如下

因为没有LinearLayout我们可以自己来自定义。刚好在网上看到有自定义好的PercentLinearlayout,分享给大家
public class PercentLinearlayout extends LinearLayout{
private PercentLayoutHelper mPercentLayoutHelper;
public PercentLinearlayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
super(context, attrs);
mPercentLayoutHelper = new PercentLayoutHelper(this);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
{
mPercentLayoutHelper.adjustChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
if (mPercentLayoutHelper.handleMeasuredStateTooSmall())
{
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b)
{
super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mPercentLayoutHelper.restoreOriginalParams();
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs)
{
return new LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
public static class LayoutParams extends LinearLayout.LayoutParams
implements PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutParams
{
private PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutInfo mPercentLayoutInfo;
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs)
{
super(c, attrs);
mPercentLayoutInfo = PercentLayoutHelper.getPercentLayoutInfo(c, attrs);
}
@Override
public PercentLayoutHelper.PercentLayoutInfo getPercentLayoutInfo()
{
return mPercentLayoutInfo;
}
@Override
protected void setBaseAttributes(TypedArray a, int widthAttr, int heightAttr)
{
PercentLayoutHelper.fetchWidthAndHeight(this, a, widthAttr, heightAttr);
}
public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
}
public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
public LayoutParams(MarginLayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
}
}
使用效果如下:
相关文章
- 下面我们来看一篇关于Android子控件超出父控件的范围显示出来方法,希望这篇文章能够帮助到各位朋友,有碰到此问题的朋友可以进来看看哦。 <RelativeLayout xmlns:an...2016-10-02
- overlay就是在地图上以另外一种形式浮现在地图上,常见的地图覆盖物为这三种类型,如:popup 弹窗、label标注信息、text文本信息等,接下来跟随小编看下openlayers6之地图覆盖物overlay详解,一起看看吧...2021-09-15
- 采用CSS覆盖的方法就可以了,但是官方是不允许这么做的...2013-10-13
Android开发中findViewById()函数用法与简化
findViewById方法在android开发中是获取页面控件的值了,有没有发现我们一个页面控件多了会反复研究写findViewById呢,下面我们一起来看它的简化方法。 Android中Fin...2016-09-20- 如果我们的项目需要做来电及短信的功能,那么我们就得在Android模拟器开发这些功能,本来就来告诉我们如何在Android模拟器上模拟来电及来短信的功能。 在Android模拟...2016-09-20
- 夜神android模拟器如何设置代理呢?对于这个问题其实操作起来是非常的简单,下面小编来为各位详细介绍夜神android模拟器设置代理的方法,希望例子能够帮助到各位。 app...2016-09-20
- 这篇文章主要介绍了vue+高德地图实现地图搜索及点击定位操作,具有很好的参考价值,希望对大家有所帮助。一起跟随小编过来看看吧...2020-09-09
- 为了增强android应用的用户体验,我们可以在一些Button按钮上自定义动态的设置一些样式,比如交互时改变字体、颜色、背景图等。 今天来看一个通过重写Button来动态实...2016-09-20
- 如果我们要在Android应用APP中加载html5页面,我们可以使用WebView,本文我们分享两个WebView加载html5页面实例应用。 实例一:WebView加载html5实现炫酷引导页面大多...2016-09-20
- 深入理解Android中View和ViewGroup从组成架构上看,似乎ViewGroup在View之上,View需要继承ViewGroup,但实际上不是这样的。View是基类,ViewGroup是它的子类。本教程我们深...2016-09-20
- 下面我们来看一篇关于Android自定义WebView网络视频播放控件开发例子,这个文章写得非常的不错下面给各位共享一下吧。 因为业务需要,以下代码均以Youtube网站在线视...2016-10-02
- java开发的Android应用,性能一直是一个大问题,,或许是Java语言本身比较消耗内存。本文我们来谈谈Android 性能优化之MemoryFile文件读写。 Android匿名共享内存对外A...2016-09-20
- TextView默认是横着显示了,今天我们一起来看看Android设置TextView竖着显示如何来实现吧,今天我们就一起来看看操作细节,具体的如下所示。 在开发Android程序的时候,...2016-10-02
- 这篇文章主要为大家详细介绍了vue+element ui实现锚点定位,文中示例代码介绍的非常详细,具有一定的参考价值,感兴趣的小伙伴们可以参考一下...2021-06-29
- 这篇文章主要介绍了React使用高德地图的实现示例(react-amap),文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友们下面随着小编来一起学习学习吧...2021-04-18
android.os.BinderProxy cannot be cast to com解决办法
本文章来给大家介绍关于android.os.BinderProxy cannot be cast to com解决办法,希望此文章对各位有帮助呀。 Android在绑定服务的时候出现java.lang.ClassCastExc...2016-09-20- 这篇文章主要介绍了Android 实现钉钉自动打卡功能的步骤,帮助大家更好的理解和学习使用Android,感兴趣的朋友可以了解下...2021-03-15
- 下面我们来看一篇关于Android 开发之布局细节对比:RTL模式 ,希望这篇文章对各位同学会带来帮助,具体的细节如下介绍。 前言 讲真,好久没写博客了,2016都过了一半了,赶紧...2016-10-02
如何根据百度地图计算出两地之间的驾驶距离(两种语言js和C#)
以下是使用js代码实现百度地图计算两地距离,代码如下所示:<script src="js/jquery-1.9.0.js" type="text/javascript" language="javascript"></script><script language="javascript" type="text/javascript" src="js/...2015-10-30基于JavaScript实现高德地图和百度地图提取行政区边界经纬度坐标
本文给大家介绍javascript实现高德地图和百度地图提取行政区边界经纬度坐标的相关知识,本文实用性非常高,代码简单易懂,需要的朋友参考下吧...2016-01-24
